Backgroud: Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is an uncommon indolent B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which has heterogeneous clinical presentations and indications for treatment. Mostly the choice of first-line therapy is based on the individual patient's characteristic and indications for treatment. In China, previous studies on WM are mostly from single-center with small sample size, limiting the information available on treatment and outcome patterns. To address this knowledge gap, we present data from an analysis based on a nationwide multicenter registry with 17-years follow-up. Our study focuses on the clinical presentation, first-line therapies, as well as outcome and prognosis of WM in China.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with WM between January 2003 and December 2019 at 35 academic hospitals in China, which have been entered in the database of the China Waldenström macroglobulinemia Registration (CWMG), were included in this retrospective study. Data including baseline clinical features, symptoms requiring treatment, treatment and survival were collected. The overall survival (OS) was defined as the duration from the diagnosis of WM to the date of death or last follow-up.
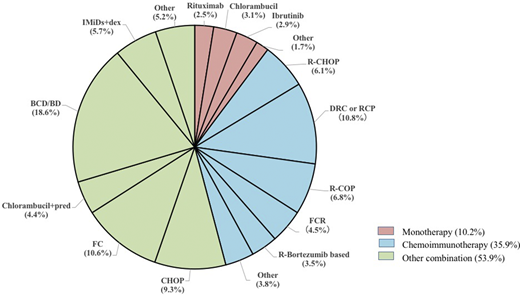
Results: Overall 1141 patients were enrolled, 829 patients were male (72.7%), with a male-to-female ratio of 2.7:1. The median age at diagnosis was 64 years (range, 29-89 years), which 472 patients (41.4%) were older than 65 years, and 126 patients (11.0%) were older than 75 years. The patients' family histories included 6 WM and 4 other lymphoproliferative disorders. Symptoms leading to treatment initiation including anemia in 828 patients (72.6%), organomegaly in 441 patients (38.7%), thrombocytopenia in 302 (26.5%), neutropenia in 246 (21.6%), constitutional symptoms in 203 (17.8%), Bing-Neel syndrome in 13 (1.1%), IgM-related symptoms in including secondary amyloidosis in 32 (2.8%), secondary autoimmune hemolysis in 25 (2.2%), peripheral neuropathy in 23 (2.0%), secondary cold agglutinin disease in 21 (1.8%), secondary cryoglobulinemia in 11 (1.0%). At the time of diagnosis, 1125 patients had full information for IPSS-WM risk stratification. Among them, 194 patients (17.2%) were classified as low risk, 436 patients (38.8%) were intermediate risk, and 495 patients (44.0%) were high risk. Overall, 734 patients had documented treatment information. 75 patients (10.2%) received monotherapy, 264 (36.0%) received chemoimmunotherapy, and 395 (53.8%) receive other combination regimens (Figure 1). The most frequently used monotherapy was chlorambucil (3.1%), followed by ibrutinib (2.9%) and rituximab (2.5%). Rituximab, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone or prednisone (DRC or RCP) were the most frequently used chemoimmunotherapy (10.8%). Followed by rituximab plus cyclophosphasmide, vincristine/vincristine and prednisone/prednisolone (R-COP) (6.8%), R-COP plus doxorubicin/epirubicin (R-CHOP) (6.1%), rituximab plus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide (R-FC) (4.5%), rituximab plus bortezomib based regimen (3.5%). Other combination regimens including bortezomib based regimen (18.6%), FC (10.6%), CHOP (9.3%), immunomodulatory drug based regimen (5.7%), chlorambucil plus prednisone (4.4%). After a median of 23 months (range 1-201 months) follow-up, 123 patients died. The estimated 5-year OS was 74.9%. Median OS were similar among patients who received monotherapy, chemoimmunotherapy or other combination regimens. To evaluate the prognostic factors of OS using multivariate Cox regression model, age > 65 years old (P=0.011, HR 0.622, 95% CI 0.431-0.898), platelet < 100×109/L (P=0.006, HR 0.570, 95% CI 0.381-0.853), serum albumin <3.5 g/dl (P=0.020, HR 0.582, 95% CI 0.369-0.918), β-2 microglobulin concentration ≥4 mg/L (P=0.019, HR 0.630, 95% CI 0.429-0.926), LDH≥250 IU/L (P=0.016, HR 0.538, 95% CI 0.326-0.890) and secondary amyloidosis (P<0.001, HR 0.277, 95% CI 0.137-0.562) at baseline had significantly shorter OS .
Conclusion: Frontline treatment choices of WM are wide heterogeneity due to various clinical presentations and the rarity of the disease. Old age, low platelet, low albumin, high β-2 microglobulin, high LDH and secondary amyloidosis indicate worse prognosis in WM. These findings may provide guidance for management of WM and better prognostic stratification of risk-adapted treatment strategies.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal